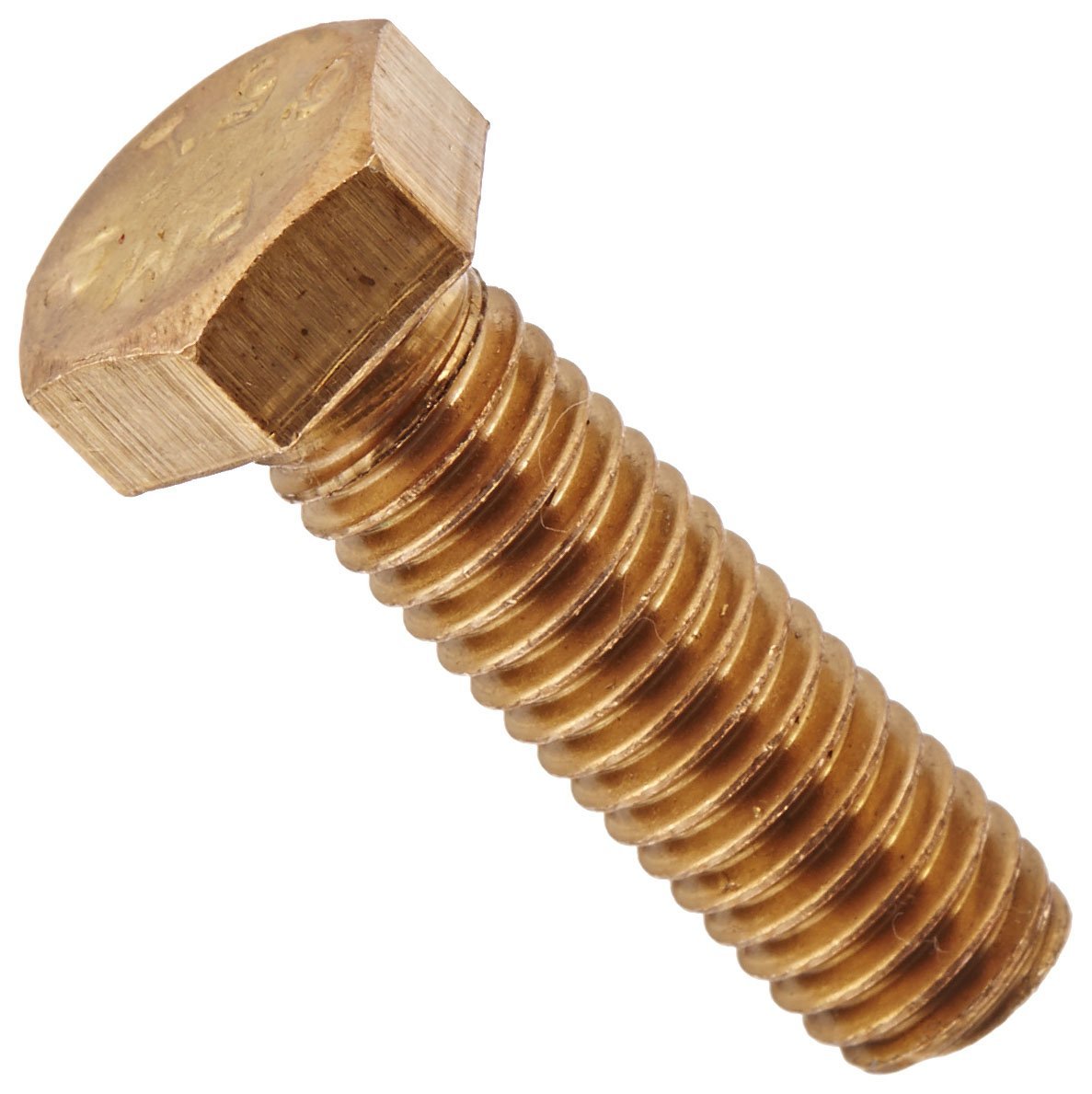
What are non-ferrous fasteners?
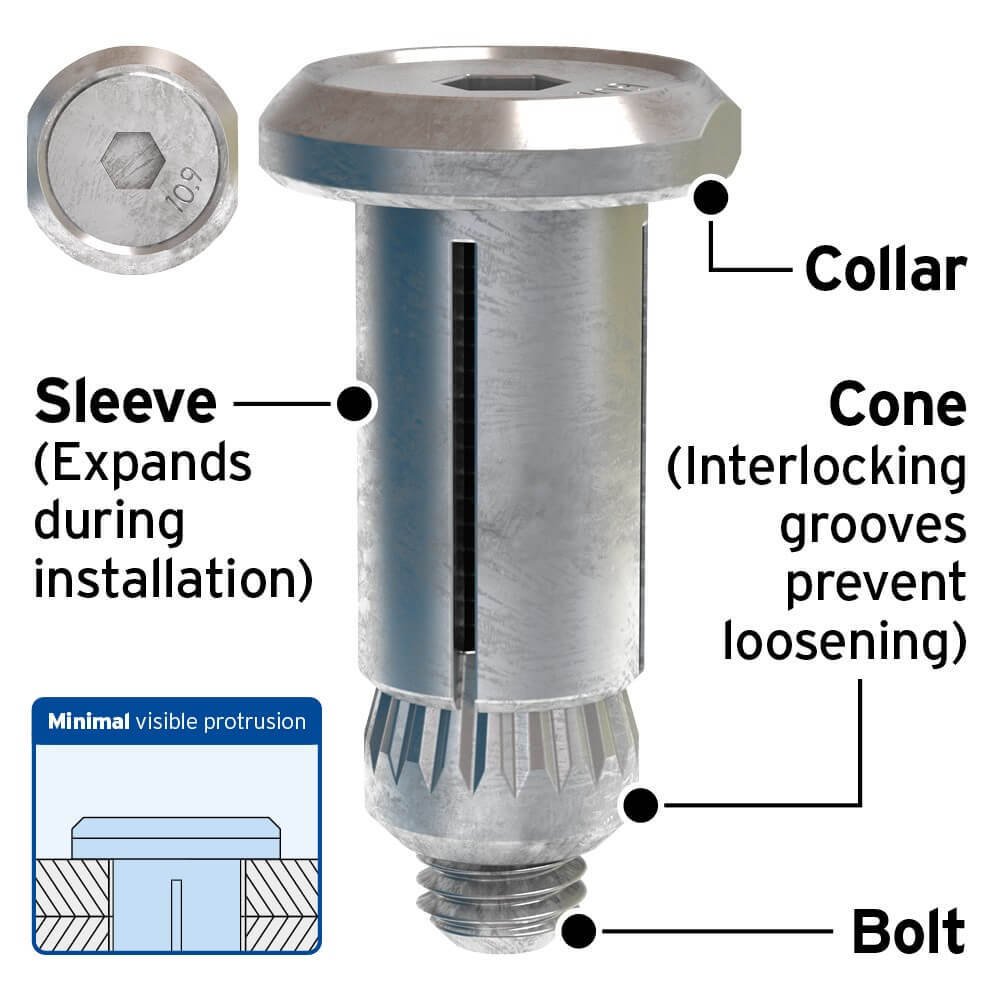
Non-ferrous fasteners are fasteners that are made from materials that do not contain iron or have very low iron content. These materials are typically more resistant to corrosion and rust than ferrous materials, making them ideal for use in applications where high corrosion resistance is required.
Common non-ferrous materials used in fasteners include brass, bronze, copper, aluminum, titanium, and stainless steel. Non-ferrous fasteners are commonly used in marine, chemical, and other corrosive environments where ferrous materials would be prone to rust and deterioration.
Some examples of non-ferrous fasteners include bolts, nuts, screws, washers, and rivets made from non-ferrous materials. These fasteners may be used in applications such as boat building, plumbing, and electronics, among others.
What are the different types of non-ferrous fasteners?
There are several different types of non-ferrous fasteners, each with their own unique properties and applications. Here are some of the most common types:
Brass fasteners: Brass is a copper alloy that is highly resistant to corrosion and has good strength and ductility. Brass fasteners are commonly used in electrical, plumbing, and marine applications.
Bronze fasteners: Bronze is another copper alloy that is known for its high strength, durability, and corrosion resistance. Bronze fasteners are often used in marine and oil and gas applications.
Copper fasteners: Copper is a highly conductive and malleable metal that is often used in electrical applications. Copper fasteners are also used in plumbing, roofing, and other applications where corrosion resistance is important.
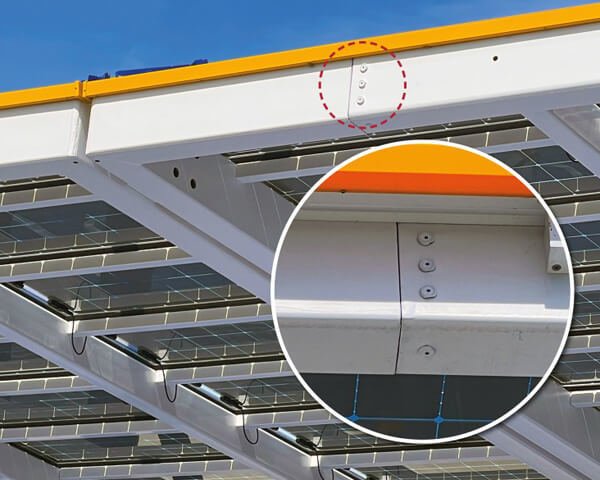
Aluminum fasteners: Aluminum is a lightweight metal that has good strength and excellent corrosion resistance. Aluminum fasteners are often used in aerospace, automotive, and construction applications.
Titanium fasteners: Titanium is a strong, lightweight metal that is highly resistant to corrosion. Titanium fasteners are commonly used in aerospace, medical, and military applications.
Stainless steel fasteners: Stainless steel fasteners are an excellent choice for outdoor applications for several reasons, including corrosion resistance, strength, longevity and aesthetics.
These are just a few examples of the different types of non-ferrous fasteners available. The choice of fastener material will depend on the specific application and the desired properties of the fastener, such as strength, corrosion resistance, conductivity, and weight.
In what applications would someone want to use non-ferrous fasteners?
Non-ferrous fasteners are often used in applications where resistance to corrosion or rust is important. This is because ferrous materials, such as steel, are prone to rust and deterioration when exposed to moisture, chemicals, and other corrosive environments.
Here are some specific applications where non-ferrous fasteners are commonly used:
Marine applications: Non-ferrous fasteners are often used in boats and other marine equipment due to their resistance to corrosion in saltwater environments.
Electrical applications: Non-ferrous fasteners are often used in electrical applications, such as wiring and circuit boards, because they are good conductors of electricity and do not corrode easily.
Chemical and petrochemical applications: Non-ferrous fasteners are often used in chemical and petrochemical processing equipment because they are resistant to the corrosive effects of chemicals.
Aerospace applications: Non-ferrous fasteners are commonly used in aircraft and other aerospace equipment due to their lightweight and corrosion-resistant properties.
Medical applications: Non-ferrous fasteners are often used in medical devices and implants due to their biocompatibility and resistance to corrosion in the body.
Outdoor and architectural applications: Non-ferrous fasteners are commonly used in outdoor structures and architectural elements, such as railings and roofing, due to their resistance to corrosion in outdoor environments.
In general, non-ferrous fasteners are a good choice for any application where the fastener will be exposed to moisture, chemicals, or other corrosive substances.
If you’d like more information about non-ferrous fasteners, contact Mudge Fasteners at (800) 634-0406 for assistance..